Intermolecular O...O Hydrogen Bonds in
E. coli L-asparaginase II Active Site
Chain A
In the active site largely made up from chain C, the aspartate ligand "flipped
over" so that the main chain carboxylate group occupied a similar position to
the side chain carboxyl group in the minimised structure. This transition occurred
rapidly and without a significant gain in energy.
All oxygen...oxygen distances between the gamma-carboxylate group and the
threonines became consistently too long for possible hydrogen bond formation by
5ps into the dynamics run.
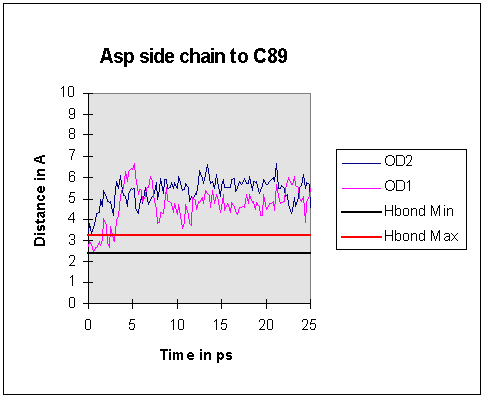
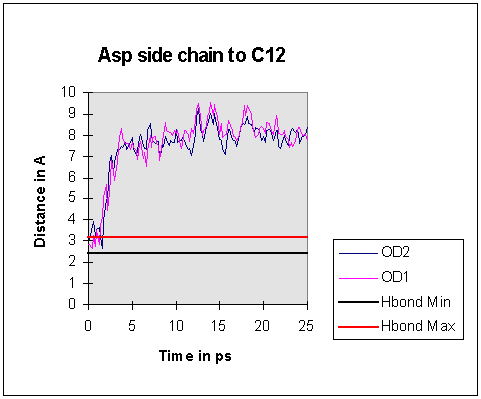
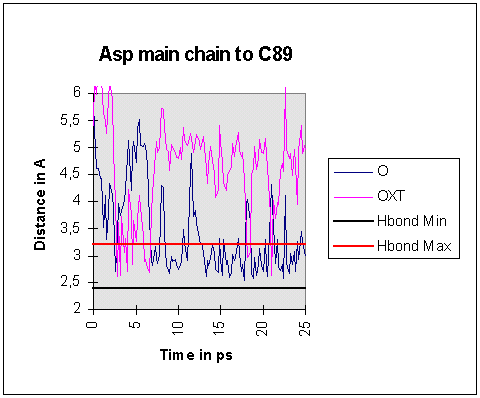
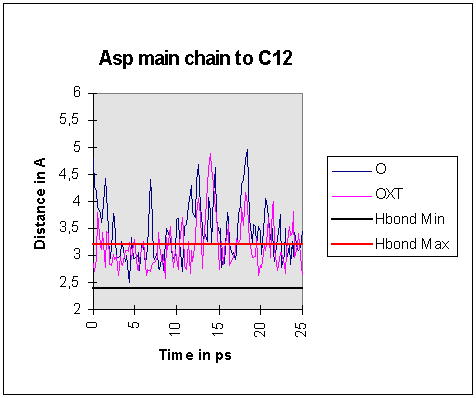
In contrast, O...O distances between the main chain carboxylate group and the
threonine hydroxyls were consistently close enough for hydrogen bonds to form
for much of the simulation.
 Back to
poster results section
Back to
poster results section





