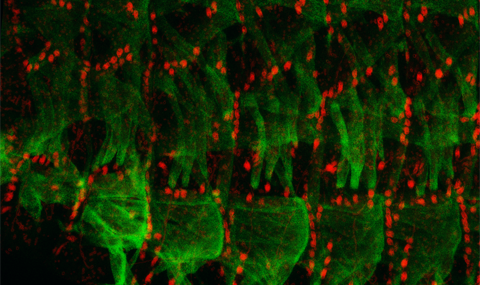
We developed a unique device, which allows to record the dynamic properties of myonuclei of individual Drosophila larval myofibers during muscle contractile/relaxation waves under the microscope. Fluorescently labeled proteins associated with the nuclear membrane, or with the chromatin are expressed specifically in larval muscles in combination with endogenous labeling of the sarcomeres. Using this setup we are able to assess dynamic changes that take place during muscle contraction in wild type or mutant muscles.
These movies demonstrate myonuclear properties in larval muscles.
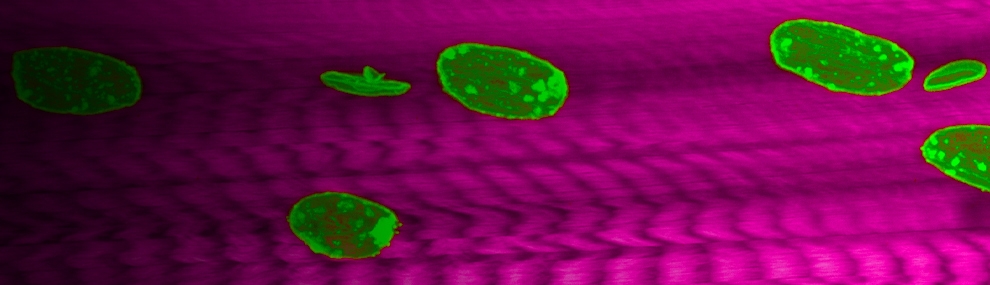
Nuclear dynamics during muscle contraction in WT and in klar/Nesprin mutant
Spontaneously contracting wild type muscle of Drosophila larva. Sarcomeric Z-lines labelled in green and nuclei in red. (Mef>mCherry-NLS; SLS-GFP). Note the equal spacing between nuclei. Images acquired with confocal spinning disk microscope in 12 fps, and the movie shown in half of its original speed. Scale bar=50µm
Spontaneously contracting klar/Nesprin mutant muscle of Drosophila larva. Sarcomeric Z-lines labelled in green and nuclei in red. (Mef>mCherry-NLS; Sls-GFP, klar). Note the nuclear clustering. Images acquired with confocal spinning disk microscope in 12 fps, and the movie shown in half of its original speed. Scale bar=50µm
Muslce contraction induced nuclear membrane deformations
Live active muscle contraction of the Drosophila larvae induces transient deformations of the myonuclei with wrinkling of the nuclear envelope. Scale bars: 10µm. Images acquired with confocal spinning disk at 8-12 fps and displayed at half of the original speed.
Lamin-C-GFP expressed in the muscle labels the myonuclear periphery and reveals oval nuclear morphology before contraction, wrinkling of the nuclear lamina induced by muscle contraction, and return to the oval shape with muscle relaxation.
BAF-GFP expressed in the muscle is localized mainly to the inner nuclear membrane but also present in the cytoplasm and the nucleoplasm (absent from the nucleolus). Similar oval nuclear morphology is observed during relaxation with muscle contraction induced wrinkling of the nuclear envelope.
klar-GFP (Nesprin) expressed in the muscle is dominant in the outer nuclear membrane but also present in the cytoplasm and the nucleoplasm (absent from the nucleolus). Again, oval nuclear morphology is observed during relaxation with muscle contraction induced wrinkling of the nuclear envelope.
Simultaneous labeling of the sarcomeric Z-lines (SLS-GFP) and the nucleoplasm (NLS-mCherry). Note the myonuclear deformation induced by sarcomeric shortening, without wrinkling of the nucleus interior.