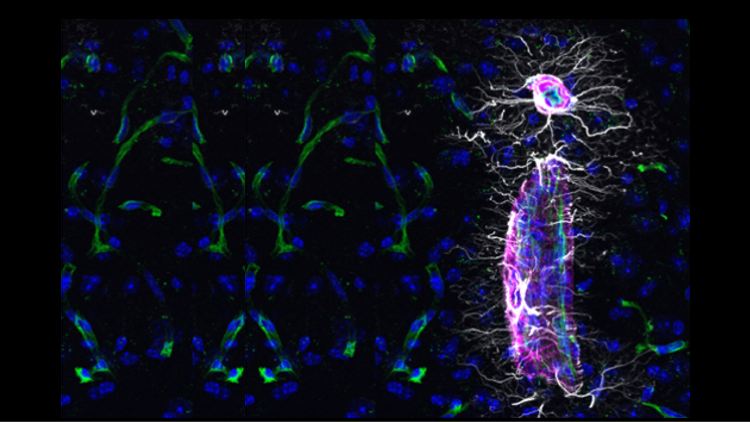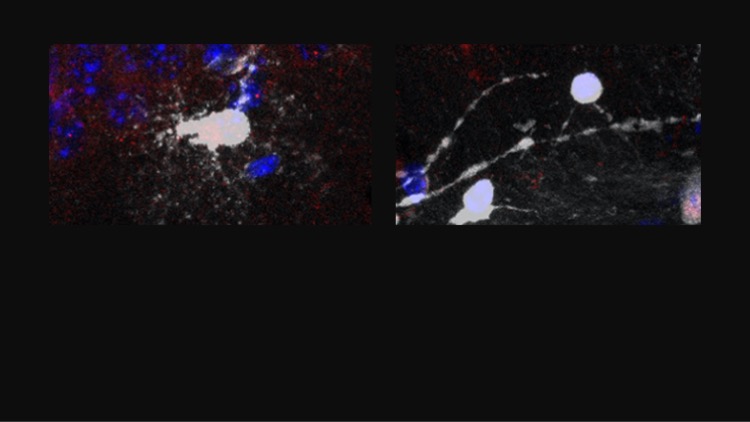
Capturing oligodendrocyte plasticity with nascent proteome tagging
Spatiotemporal regulation of protein synthesis underlies neuronal plasticity in learning and memory. The development of spatiotemporal tools that enable real-time control of neuronal excitability and inhibition have led to deep mechanistic understanding of neuronal and synaptic plasticity. However, it is unclear what are the mechanisms that regulate activity-dependent oligodendrocyte plasticity. We have recently generated oligodendrocyte specific bio-orthogonal mice that allow us to track oligodendrocyte specific proteomes and secretomes with unprecedented temporal control. We aim to identify stage specific dynamic processes occurring in oligodendrocyte lineage cells during memory formation with the goal of identifying regulators of OL plasticity. This knowledge could be used to develop tools to directly manipulate oligodendrocyte lineage cells.