Parallel processing - passive touch
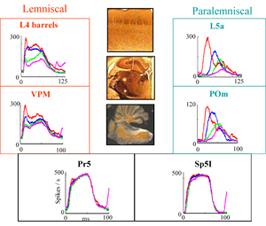
These results were obtained by recording neuronal activity in anesthetized rats while applying mechanical stimuli to passive whiskers. Natural active touch in awake rats involves motor-driven sensory acquisition and rats actively move their whiskers to sample the world near their snout. To study active whisking with controlled stimulus application, we developed a technique of artificial whisking in anesthetized rats.
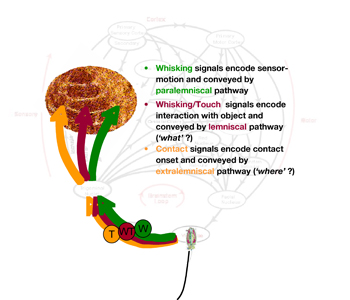
Parallel processing - active touch
Relevant papers
-
(2006). Layer-specific touch-dependent facilitation and depression in the somatosensory cortex during active whisking. Journal Of Neuroscience. 26:9538-9547.
-
(2006). Parallel thalamic pathways for whisking and touch signals in the rat. Plos Biology. 4:819-825.
-
(2000). Transformation from temporal to rate coding in a somatosensory thalamocortical pathway. Nature. 406:302-306.
-
(2015). Coding of Object Location in the Vibrissal Thalamocortical System. Cerebral Cortex. 25:563-577.


