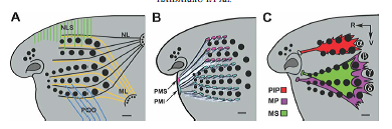
We described four superficial extrinsic muscles and five parts of the M. nasolabialis profundus. The connection scheme of the three parts of the M. nasolabialis profundus is described here for the first time. These muscles are inserted into the plate of the mystacial pad, and thus, their contraction causes whisker retraction. All the muscles of the rat mystacial pad contained three types of skeletal striated fibers (red, white, and intermediate). Although the entire rat mystacial pad usually functions in unisom, our data revealed its structural segmentation into nasal and maxillary subdivisions.
The mechanisms of whisking in the rat, and hypotheses concerning biomechanical interactions during whisking, are discussed with respect to the muscle architecture of the rat mystacial pad.
Relevant papers
-
(2010). Muscle Architecture in the Mystacial Pad of the Rat. Anatomical Record-Advances In Integrative Anatomy And Evolutionary Biology. 293:1192-1206.
-
(2011). Collagenous Skeleton of the Rat Mystacial Pad. Anatomical Record-Advances In Integrative Anatomy And Evolutionary Biology. 294:764-773.
-
(2012). Dorsorostral Snout Muscles in the Rat Subserve Coordinated Movement for Whisking and Sniffing. Anatomical Record-Advances In Integrative Anatomy And Evolutionary Biology. 295:1181-1191.
-
(2013). Mediation of Muscular Control of Rhinarial Motility in Rats by the Nasal Cartilaginous Skeleton. Anatomical Record-Advances In Integrative Anatomy And Evolutionary Biology. 296:1821-1832.
-
(2015). Muscles Involved in Naris Dilation and Nose Motion in Rat. Anatomical Record-Advances In Integrative Anatomy And Evolutionary Biology. 298:546-553.


