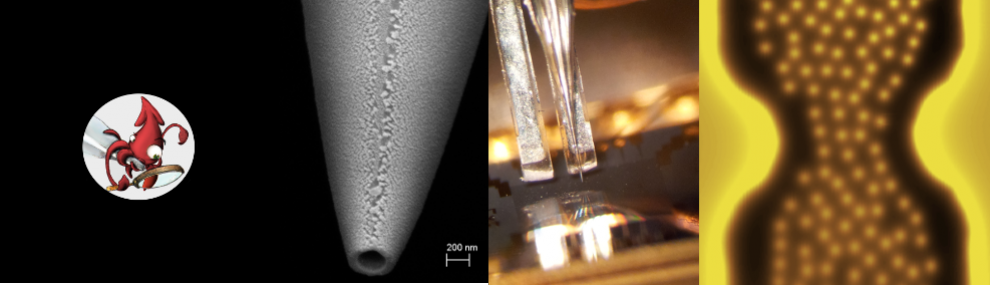
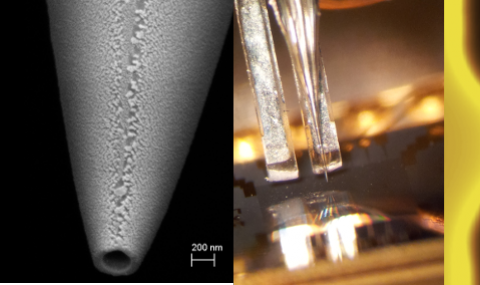
This image shows a schematic view of the magneto-optical system. The magneto-optical indicator, which is an iron-garnet film with an in-plane magnetization, is placed on top of a superconductor sample. A linearly polarized light is reflected from the bottom mirror of the indicator and undergoes a Faraday rotation within the indicator. The angle of rotation of the polarization is proportional to the local magnetic field.
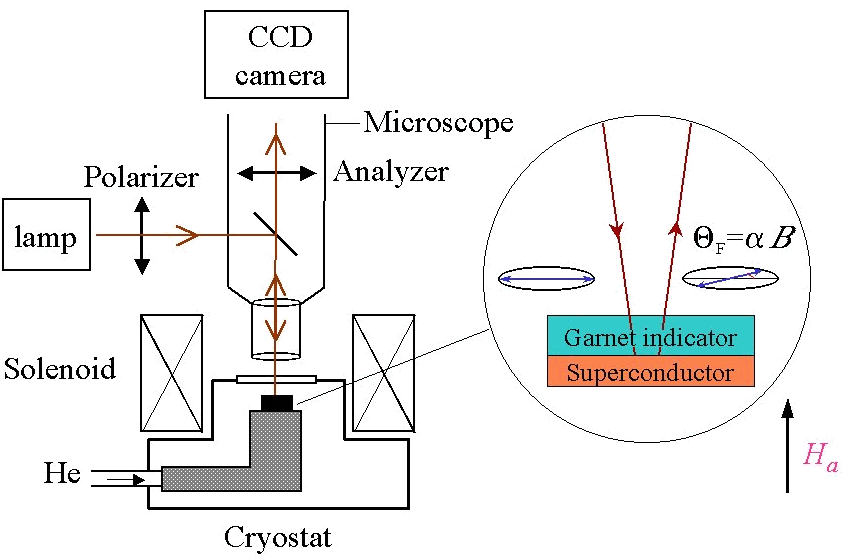
Schematic drawing of the magneto-optic measurement setup
After passing through a perpendicularly polarized analyzer, a real time optical image is obtained, in which the local brightness is directly related to the intensity of the local magnetic field. The resulting image is captured by a CCD camera and is transferred to a computer. In order to improve the field sensitivity of the technique we have developed a differential MO method.