More than four decades have passed since ABC transporters were identified as the culprit of multidrug resistance (MDR). Extensive studies led to development of highly effective inhibitors of the ABC transporters, but so far these inhibitors failed in clinical trials. We explored the possible existence of MDR mechanisms other than drug transport. Major chemotherapeutic agents, including doxorubicin, 5-FU, vincristine and bortezomib trigger extensive endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress. We observed that MDR tumor cells are also resistant to ER stress-triggered cell death, suggesting that ER stress is an important mechanism by which chemotherapy kills tumor cells. The transcription factor C/EBP beta is over-expressed in many tumor types, naturally appearing in two isoforms: a full size active form termed LAP, and a dominant negative truncated form termed LIP. Previously, we demonstrated that LAP augments tumor progression by attenuating ER stress-triggered cell death, whereas LIP attenuates tumor progression by enhancing ER stress-triggered cell death. We now find that a broad range of MDR cell lines, as well as primary MDR tumor cells, lack LIP (Fig. 1). Importantly, restoring LIP abolished the chemoresistance in all of these MDR cell types (Fig. 2). On further analysis, we discovered that LIP mRNA expression was identical in chemosensitive cells and in their drug-selected MDR subclones. However, LIP was rapidly degraded by proteasomal and lysosomal proteases in the MDR cells and not in the chemosensitive cells. We then demonstrated that proteasome and lysosome inhibitors attenuated LIP degradation in MDR cells, rendering them more sensitive to chemotherapy. A combination of such inhibitors, currently used in the treatment of myeloma (bortezomib, carfilozumib), and malaria (chloroquine), should be explored as potential means for reversing MDR.

Fig. 1. Multidrug resistant subline (HT29/MDR) of human colon carcinoma cell line (HT29) does not express C/EBP-β LIP or other ER stress markers under ER stress or chemotherapy.
Glossary: eIF2α, eukaryotic initiation factor 2α; peIF2α, phosphorylated eIF2α; C/EBPβ LAP, CCAAT/enhancer binding protein β liver-activating protein; C/EBPβ LIP, C/EBPβ liver inhibitory protein; CHOP, C/EBPβ homologous protein; Pgp, P-glycoprotein (a multidrug transporter); MRP1, MRP2, multidrug resistance proteins 1 & 2.
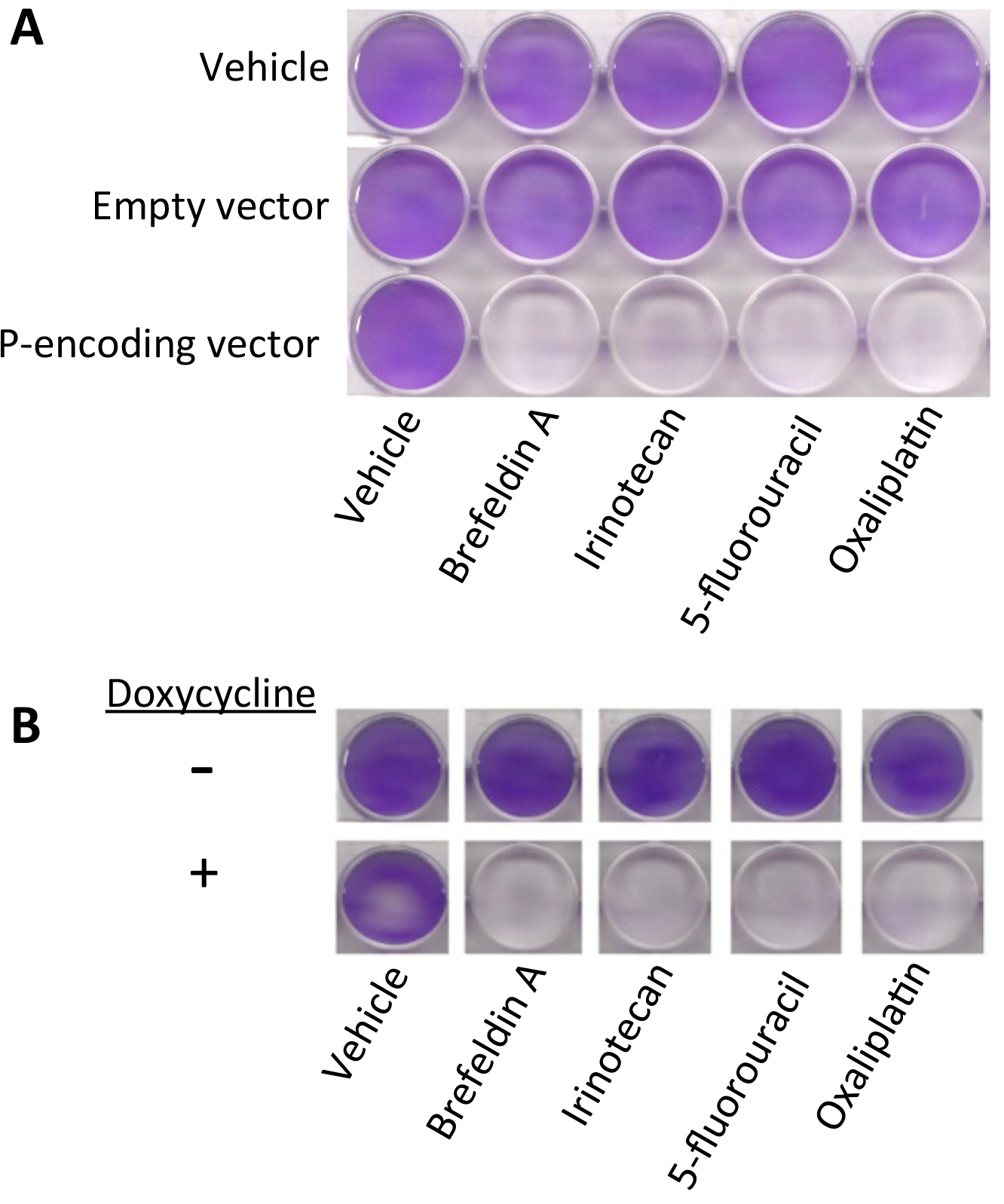
Fig. 2. Vector-mediated (A) or inducible (B) C/EBPβ LIP expression restores the response of HT29/MDR cells to ER stress (brefeldin A) and to chemotherapy (irinotecan, 5-fluorouracil and oxaliplatin). (live cells are stained purple with crystal violet).

